RAID 0 Recovery Expertise
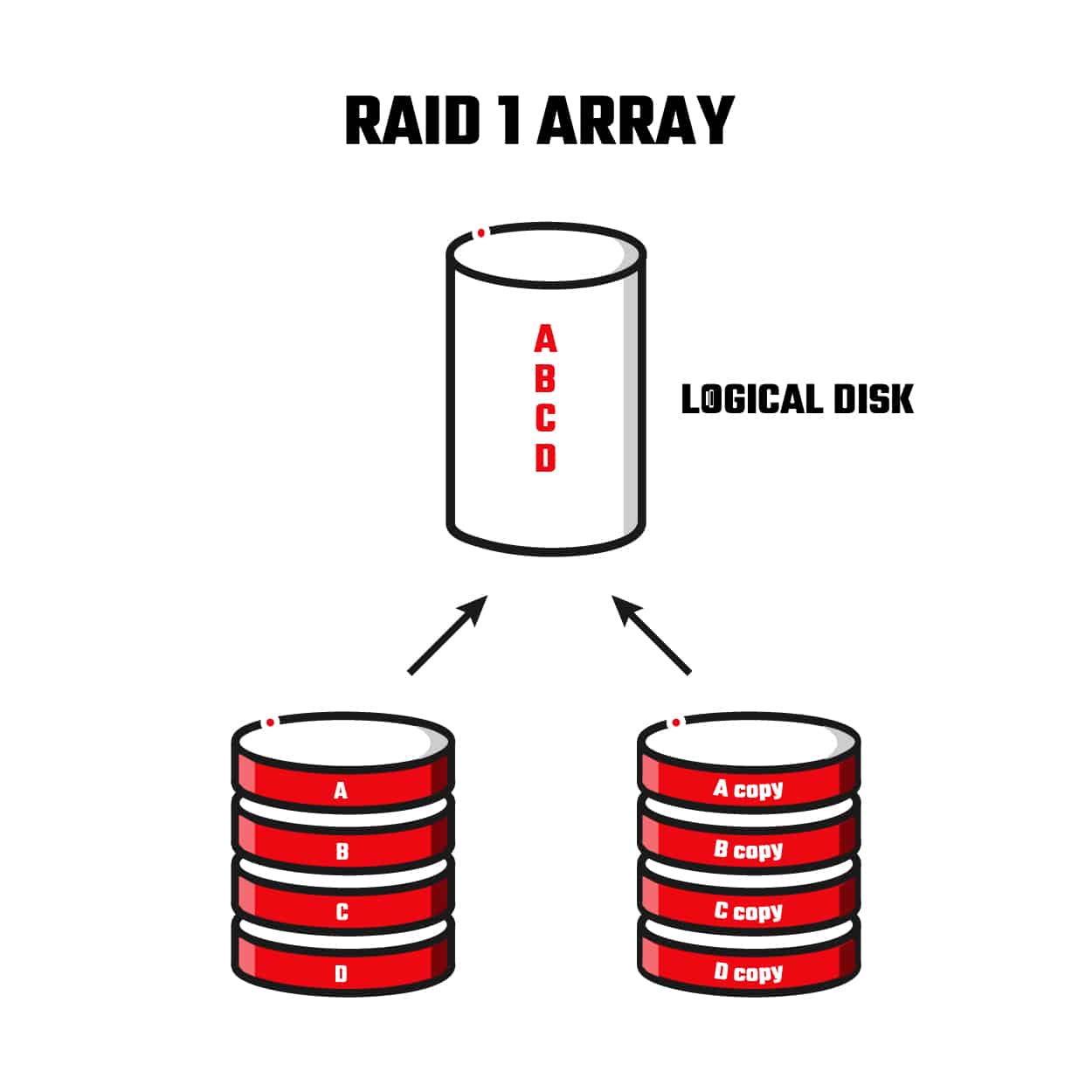
RAID 0 splits (“stripes”) data evenly across two or more hard drives without parity information, redundancy, or fault tolerance. This makes is a fairly simple system to set up. However, because RAID 0 provides no fault tolerance or redundancy, the failure of one drive will cause the entire array to fail since data is striped across all disks. The main reason a RAID 0 configuration is typically implemented is because of speed and performance. Caching live streaming video and video editing are common uses for RAID 0 due to speed and performance.
Since RAID 0 does not use data redundancy, the failure of any physical drive in the striped disk set results in the loss of the data on the striped unit and, consequently, the loss of the entire data set stored across the set of striped hard disks. In such a case data recovery is the only option to prevent permanent loss of data.
All RAID Servers and Configurations Supported
DriveSavers specializes in RAID data recovery, offering unmatched expertise for all RAID server levels and configurations. Whether you’re dealing with hardware like HDDs and SSDs or specific RAID setups from RAID 0 to RAID Z3, our services encompass a broad spectrum of RAID servers and media across major brands like HP, Dell, and IBM.
Trust DriveSavers for reliable recovery of your critical RAID data.

All Hardware Types
Including HDDs, SSDs, NAND Flash, and interfaces like PATA/SATA, SAS, SCSI, iSCSI, eSATA, PCI, and PCIE.
All RAID Makes
Standalone systems, SAN, NAS, HP ProLiant, Dell PowerEdge, IBM xSeries, Supermicro, Intel, AMD, EMC, and NetApp, and more.
Data Recovery Options
At DriveSavers, our skilled team is just a phone call away. They’ll work with you directly to discuss the best recovery solution for your needs. While most of our work is conducted at our secure California facility, we recognize that some complex server configurations, such as RAID, NAS, and SAN systems, may necessitate more flexible options to address specific challenges. We offer multiple solutions to accommodate your needs, with the utmost consideration for your company’s security protocols and any relocation limitations.
In-Lab
Most devices are sent for data recovery to our certified secure lab for our Economy, Standard, or Priority data recovery service.
Remote
DriveSavers provides a secure Remote Data Recovery service for many data loss situations that do not involve mechanical or physical damage.
Onsite
The Onsite Data Recovery service is available for devices with any data loss scenario, including mechanical or physical damage.
Companies Worldwide Trust DriveSavers
DriveSavers supports over 20,000 business partners worldwide. Your business could be one of them! Some of our satisfied customers include companies such as Coca Cola, Facebook, Google, AT&T, Sony, NASA, and many others. Learn more.
Data Security
During Data Recovery
In the virtual world of the web, other data recovery companies may claim to provide the same levels of experience, service, and security as DriveSavers. But, can they really support what they say? DriveSavers provides proof. Learn more.

Experts You Can Trust
With over 40 years in the business, our RAID data recovery engineers possess deep technical know-how, ensuring the best RAID recovery rate in the industry. We’re specialists in retrieving data from all operating systems and high-capacity devices, including RAID systems, NAS, SAN, and multi-disk servers. DriveSavers is the data recovery service you can rely on. We consistently save lost databases, ERP accounting systems, mail servers, and a wide range of mission-critical data for organizations of all sizes.
RAID devices vary depending on their manufacturer. DriveSavers engineers have an in-depth understanding of each manufacturer’s unique components and configurations. Our technical partnerships with RAID systems and controller manufacturers grant us exclusive access to methods, tools, and technologies that aid in RAID data recovery from SSDs, HDDs, and intricate hybrid storage systems.
Manufacturer Approved
All leading manufacturers authorize DriveSavers to open sealed storage device mechanisms without voiding the original warranty. Our data recovery allows you to receive an in-warranty device replacement from the manufacturer. Learn more.
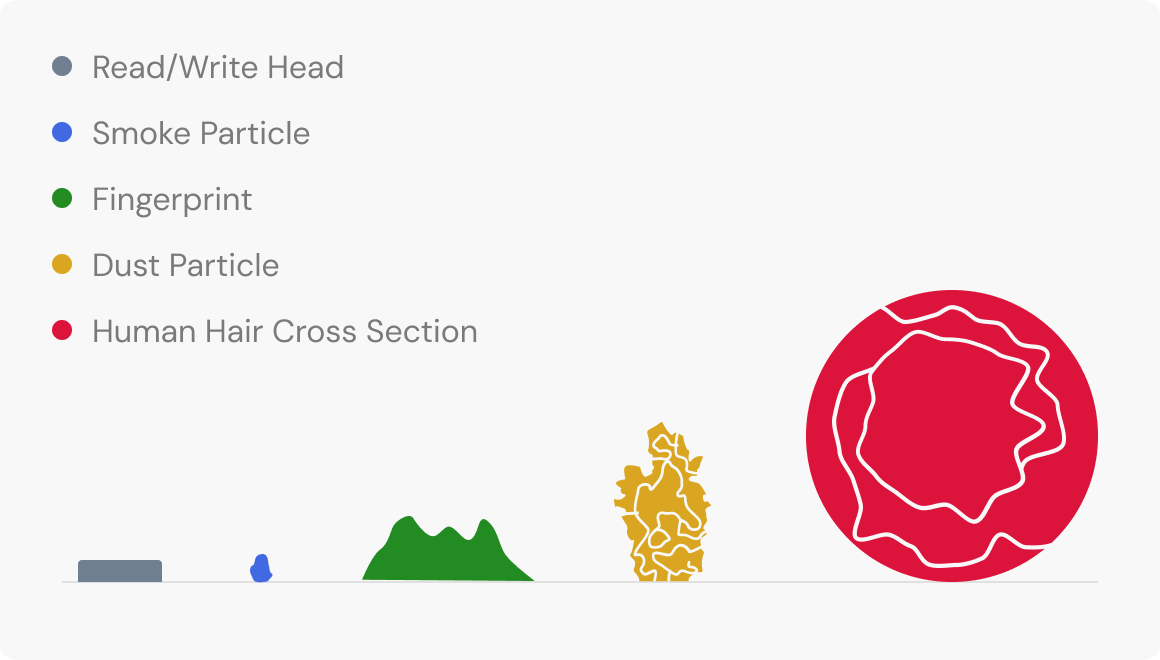
Certified ISO Cleanroom Maximizes Recovery Results
DriveSavers operates the industry’s largest state-of-the-art Certified ISO Cleanroom environment. To ensure the best possible outcomes in data recovery, all hard disk drive physical recovery operations take place in the DriveSavers state-of-the-art Cleanroom setting — the industry’s pinnacle of controlled environments.
The Certified ISO Class 5 Cleanroom adheres to the guidelines established by top-tier hard drive and data storage manufacturers. This is where DriveSavers engineers conduct a detailed examination of malfunctioning HDDs, assess them for physical defects, and carry out precise component-level repairs. Our recovery methods won’t invalidate the original hard drive warranty.
This image details the importance of opening a hard disk drive in an ISO-certified cleanroom. Tiny airborne particles can accumulate on the open hard disk drive platters, causing read-write heads to malfunction and damage the platter surface during the recovery process. Learn more.

X-Ray Technology
DriveSavers utilizes X-ray technology for precise diagnostics, identifying irregularities and critical damage in storage media without risking device integrity. Using X-ray technology expands our data recovery capabilities, confirms suspected component failure, and validates proficiency of ball grid array (BGA) rework. No other data recovery service has this advanced technology in its lab.

Why RAIDs Fail
RAIDs can fail for various reasons, including hardware malfunctions, human errors, software glitches, and application mishaps. Whether you need RAID array or RAID drive data recovery, we are here to support you.
- Corrupted RAID configuration
- Environmental damage (lightning, flood, fire)
- Physical abuse or vibration damage
- Overheating
- Intermittent or multiple drive failure
- Power issues (spike, supply burnout/failure, circuit malfunction)
- RAID controller failure
- Drive incompatibility
- Damaged connector
- Manufacturer defect
- Accidental deletion or reformatting (files, drives/array, partitions)
- Incorrect media replacement
- Overwritten files, databases, or RAID settings
- Employee sabotage
- Lost/forgotten password
- Incorrect RAID setup
- Backup or software failures
- Virus or worm infection
- Corrupt or missing files/data
- Directory or firmware corruption
- Configuration errors (server registry, RAID)
- Unable to load or run files
- Corrupted or locked databases
- Deleted tables

Call DriveSavers Day or Night
Call now to receive a quote and a clear recovery plan. Same-day assessment is available. Cost is confirmed before the work begins.
















